Compelling User experiences (UX) are no longer created by static designs or even traditional data-driven insights, they’re created dynamically, adapting to users’ behaviors and anticipating their needs in real time. From adaptive personalization to real-time decision-making frameworks, generative AI can create a UX that evolves based on context, location, behavior, and even emotional cues.
In this blog, we’ll explore how the fusion of AI and UX is reshaping design and what benefits and challenges come with using AI in this field.
What’s Changed with Generative AI – Mindset, Process or Design?
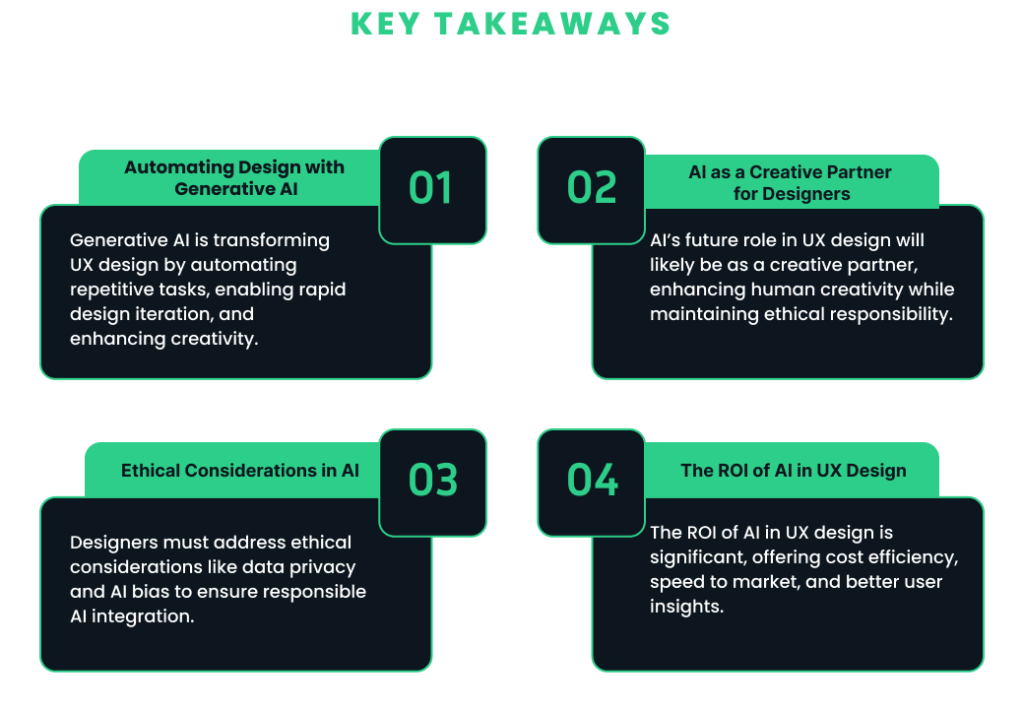
Generative AI has transformed UX design by shifting designers from intuition-based approaches to data-driven insights, encouraging a more analytical mindset. Collaboration has become easier, as teams can share ideas and feedback in real-time, speeding up the workflow. Additionally, the continuous gathering and analysis of user data allows for ongoing refinements, making designs more responsive to user needs.
The role of designers is also evolving; they’re blending traditional design skills with data analysis and machine learning knowledge. The combination of AI’s data-driven precision and the creative nature of UX allows them to work smarter, faster, and more creatively.
Which means:
- Automating the creation of elements like layouts, buttons, and color schemes.
- Simulating user interactions to identify potential pain points.
- Focusing on high-level strategy while letting AI handle time-consuming, detail-oriented tasks.
How AI Algorithms are Transforming User Experiences
One of the most exciting contributions of AI to UX is personalization. By analyzing vast amounts of user behavior data, AI can create personalized experiences that increase engagement and satisfaction. This is particularly relevant in industries like e-commerce, financial services, and social media, where tailored experiences lead to higher retention and loyalty.
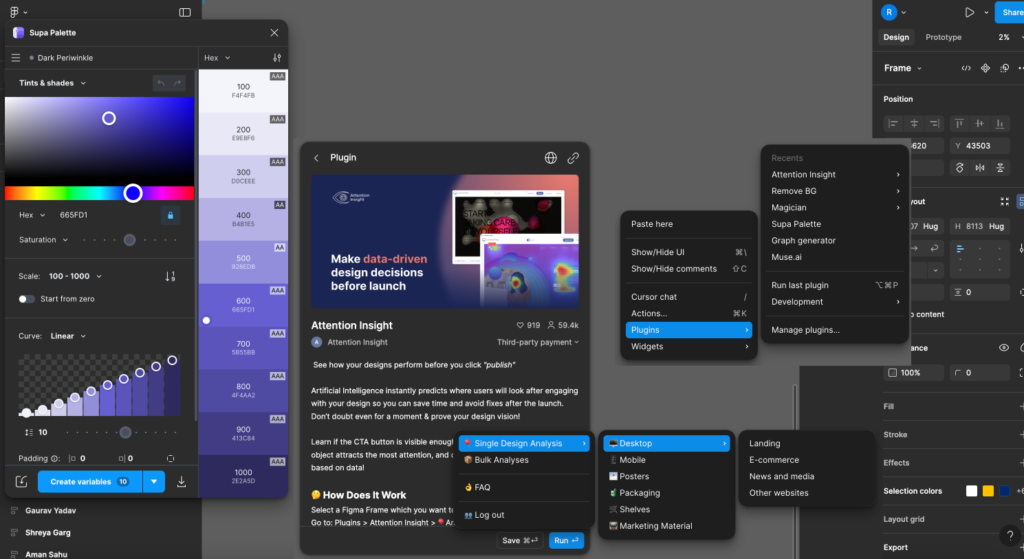
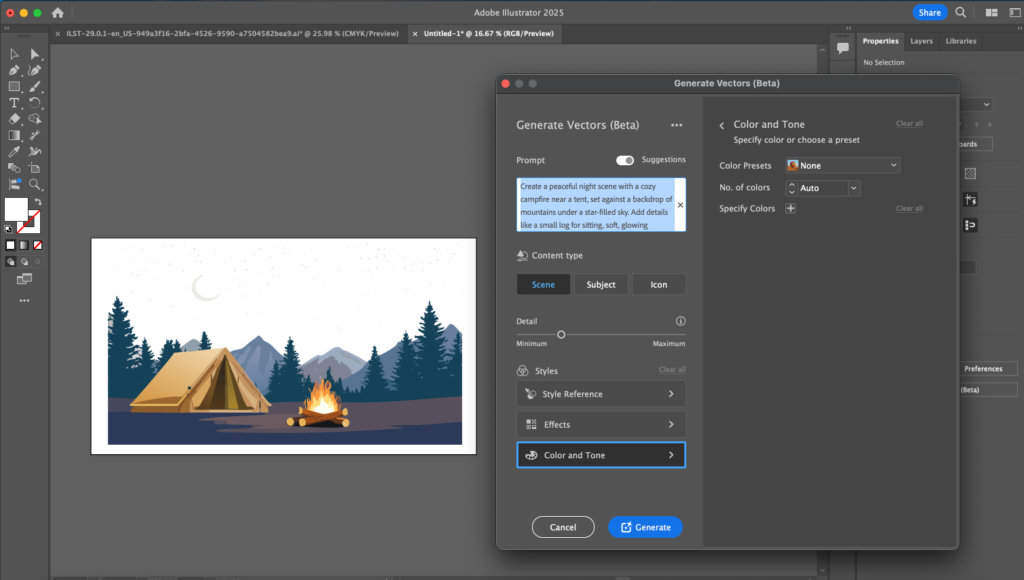
Tools like Figma’s AI plugins or Adobe’s AI-enhanced features enable designers to automatically generate design elements based on data, accelerating the design process. By creating multiple design iterations, Generative AI helps designers make informed decisions grounded in user interaction patterns.
Benefits of Generative AI in UI Design
1. Enhanced Creativity and Inspiration
Generative AI can analyze design trends and explore unique concepts, giving designers a broader range of creative inspiration. This allows them to push creative boundaries and come up with ideas that may not be immediately apparent, fostering innovation. For example, tools like Adobe Sensei can suggest innovative layouts or color palettes based on emerging design patterns.
2. Speed and Efficiency
AI automates tasks like layout creation, icon generation, and color selection, freeing designers to focus on higher-level creative decisions. This boosts the overall efficiency of the design process and shortens the time to project completion. Figma’s AI tools can quickly generate multiple design variations, reducing the time spent on routine tasks and enabling teams to deliver results more quickly.
3. Consistency Across Designs
One key advantage of AI tools is their ability to maintain visual consistency across all design components, such as buttons, icons, and menus. Tools like Sketch’s Libraries can automatically update design elements across different files, ensuring that components like buttons, icons, and menus align visually. This prevents discrepancies that often arise when different designers handle various aspects of a project, ensuring a cohesive look and feel.
4. Data-Driven Design Decisions
AI systems can process large datasets to inform design choices, making the process more strategic. Google Analytics for instance, can provide insights on user behavior, allowing designers to tweak their interfaces based on actual usage patterns. This ensures that design decisions are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and data-backed, leading to more user-centered designs.
5. Personalization and Enhanced User Engagement
By generating designs tailored to specific user preferences, AI helps create personalized interfaces that increase user engagement and satisfaction. Platforms like Spotify use AI algorithms to analyze user listening habits, generating customized playlists and recommendations. Personalization is key in competitive markets where meeting individual user needs can lead to greater user loyalty.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven UX Design
While AI offers remarkable advantages, its use also introduces significant ethical challenges. UX designers need to ensure that AI systems are transparent, free from bias, and respect user data privacy.
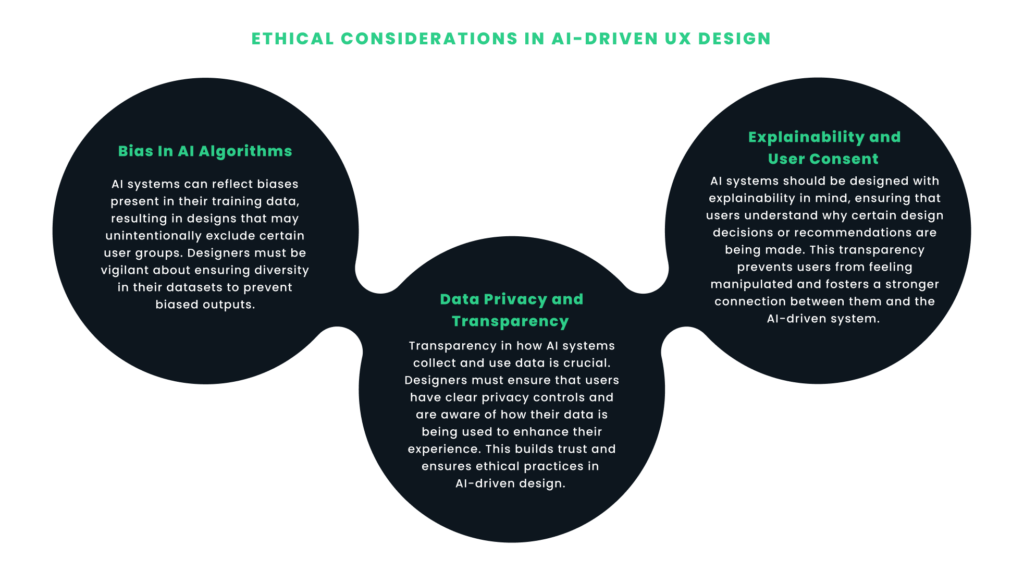
1. Bias in AI Algorithms
AI systems can reflect biases present in their training data, resulting in designs that may unintentionally exclude certain user groups. Designers must be vigilant about ensuring diversity in their datasets to prevent biased outputs.
2. Data Privacy and Transparency
Transparency in how AI systems collect and use data is crucial. Designers must ensure that users have clear privacy controls and are aware of how their data is being used to enhance their experience. This builds trust and ensures ethical practices in AI-driven design.
3. Explainability and User Consent
AI systems should be designed with explainability in mind, ensuring that users understand why certain design decisions or recommendations are being made. This transparency prevents users from feeling manipulated and fosters a stronger connection between them and the AI-driven system.
Challenges of Using AI in UI Design
1. Potential Lack of Originality
AI systems often draw from existing patterns and datasets, which can result in designs that lack originality. This reliance on established designs may lead to repetitive or generic outputs that don’t stand out creatively.
2. Difficulty in Understanding Context
AI tools may struggle to fully grasp the nuances of user needs and design context. While AI excels at automating tasks, it lacks the intuition to understand cultural or emotional subtleties that influence design decisions.
3. Absence of Human Touch
AI-generated designs, while efficient, often lack the emotional depth and personal insights that human designers bring. Empathy and personal experience are critical in creating meaningful user interfaces that truly connect with audiences.
4. Ethical Concerns
AI’s reliance on data raises concerns about algorithmic bias and fairness. Without proper oversight, AI could perpetuate exclusionary designs. Designers need to ensure AI systems are trained on diverse datasets to promote fairness and inclusivity.
AI and the ROI of UX Design
The investment in AI for UX design offers substantial returns on investment (ROI). Generative AI accelerates processes like wireframing, A/B testing, and prototyping, reducing the time and effort required to bring products to market. This leads to cost efficiency and faster project completion, allowing companies to optimize user engagement.
By providing deep insights into user behavior, AI also enables companies to continuously refine designs, predicting user needs more accurately without extensive manual testing.
Will AI Replace Designers or Become Their Creative Partner?
A question that often arises in discussions about AI’s role in UX is whether it will replace designers. While AI can automate certain tasks and streamline workflows, it cannot replicate the creativity, empathy, and nuanced understanding of human interactions that designers bring to their work.
UX design relies heavily on human intuition and emotional intelligence, aspects where AI still falls short. Designers navigate complex social contexts and subjective user preferences—tasks that require a human touch. Rather than replacing designers, AI will augment their capabilities, enabling them to focus on strategy, creativity, and human-centered design.
While AI handles the repetitive, data-intensive tasks, designers will have more freedom to anticipate user needs and create innovative solutions that scale across large user bases. The future of UX will likely be defined by a collaborative relationship between human creativity and AI-driven insights.
Contributed By
Rishabh Srivastav | UI/UX Designer

